2nd puc computer science model question papers and answers,2nd puc computer science solved model question papers
Maxterms: “The product of all the literals with or without bar in the logic system is called maxterms”.
In this method the elements are stored column wise, i.e. m elements of first column are stored in first m locations, m elements of second column are stored in next m locations and so on. E.g.
A 3 x 4 array will stored as below:
-Backup and recovery: RDBMS provides backup
and recovery subsystem that is responsible for recovery from hardware and
software failures. For example, if the failure occurs in between the
transaction, the RDBMS recovery subsystem either reverts back the database to
the state to the previous state of the transaction or resumes the transaction
from the point it was interrupted so that its complete effect can be recorded
in the database.
There are two types of power supply connected to a computer system; they are Switched Mode Power Supply (SMPS) and Uninterruptable Power Supply (UPS).
- SMPS: it converts AC power into DC power. It is a metal box in the rear of the system. It contains the power card plug and a fan for cooling, because it generates a lot of heat. SMPS with a power of 300 watts is needed. It converts 230 volts of AC to 5 to 12 DC volts and the wattage is around 180 to 300 watts, 450 watts and 500 watts.
- UPS: An UPS is a power supply that includes a battery to maintain power in the event of a power failure. An UPS keeps a computer running for several minutes to few hours after a power failure, enabling us to save data the is in RAM and then shut down the computer.
There are two types of UPS: Online UPS and standby UPS.
- Online UPS: it provides continuous power to the system from its own inverter when the power goes off. For a PC with color monitor 15”, requires an UPS of 500 VA and for a PC with color monitor 17”, requires an UPS of 600 VA.
- Standby UPS or Offline UPS: it monitors the power line and switches to battery power as soon as it detects a problem. The switch over to battery however, can require several milliseconds, during which time the computer is not receiving any power.
Ans: - stack is used to reverse a word.
public: void getdata();
void putdata();
};
- Authentication: Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user by obtaining some sort of credentials and using those credentials to verify the user's identity. If the credentials are valid, the authorization process starts. Authentication process always proceeds to Authorization process.
- Encrypted smart cards: Confidentiality is the use of encryption to protect information from unauthorized disclosure. Plain text is turned into cipher text via an algorithm, then decrypted back into plain text using the same method.
Cryptography is the method of converting data from a human readable form to a modified form,
and then back to its original readable form, to make unauthorized access difficult.
- Biometric systems: it involves unique aspects of a person’s body such as finger prints, retinal patterns, etc to establish his/her identity.
- Firewall: A firewall is a network security system designed to prevent unauthorized access to or from a private network. Firewalls can be implemented in both hardware and software, or a combination of both. Network firewalls are frequently used to prevent unauthorized internet users from accessing private networks connected to the Internet, especially intranets. All messages entering or leaving the intranet pass through the firewall, which examines each message and blocks those that do not meet the specified security criteria.
- Multilevel inheritance: the classes can also be derived from the classes that are already derived. This type of inheritance is called multilevel inheritance.
PU-II COMPUTER SCIENCE
SOLVED MODEL QUESTION PAPER 5
PART - A
I. Answer all the questions. Each question
carries 1 mark. 10 x
1 = 10
1. What is Data bus?
Ans: a bus is a set of wires and each wire carry one bit of data.
2. Write the standard symbol for two input NOR
gate.
Ans:
3. What is sorting?
Ans: the process of arrangement of
data items in ascending or descending order is called sorting
4. Define the term ‘topology’ of computer
networks.
Ans: the actual
appearance or layout of networking.
5. Which symbol is used as address operator in
C++?
Ans: Address of
(&)
6. What is a record?
Ans: A single entry
in a table is called a record.
7. What is a virus?
Ans: computer
virus is a malicious program that requires a host and is designed to make a
system sick.
8. Name any one non-linear data structure.
Ans: trees and graphs.
9. Mention any one type of e-commerce.
Ans: business to
business, business to consumer.
10. Expand ISA.
Ans: Industry Standard Architecture.
PART – B
II.
Answer any five questions. Each question
carries 2 marks. (5
X 2 = 10)
11. State and
prove Involution law.
Ans:
it states
that the complement of a variable is complemented again, we get the same
variable.
~(~X)=X.
proof: if x=0 then ~x=1 and ~(~x) = ~1 = 0 = x
if x=1 then ~x=0 and ~(~x) = ~0 = 1 = x
12. Prove
X.(X+Y)=X.
Ans: : LHS = X.(X+Y)
= X.X+X.Y
= X+XY
= X(1+Y)
= X.1
= X
=RHS
13. What are
minterms and maxterms?
Ans: Minterms: “The sum of all the literals with or
without bar in the logic system is called minterms”. Maxterms: “The product of all the literals with or without bar in the logic system is called maxterms”.
14. What is
destructor? Write the symbol used for destructor.
Ans: Destructor is a
special member function which is used to de-allocate memory location occupied
by the object created by the constructor.
Symbol used for
destructor is tilde (~).
15. Mention the
types of data files.
Ans: text file and
binary file
16. What is
Database Management System? Give an example of DBMS software.
Ans: DBMS is a
software that allows creation, definition and manipulation of database.
Example: Oracle,
Sybase, DB2, Ingress, Informix, MS-SQL server
17. Write any
two member functions belonging to ofstream class.
Ans: put(), write().
18. Define:
a)
Client
b)
Server.
Ans: Client is a computer system that seeks
data and information from the other computer.
Server is a computer
system that provides data and information to the other computer.
PART – C
III.
Answer any five questions. Each question
carries 3 marks. (5
X 3 = 15)
19. Explain any
three I/O ports.
Ans: - serial port or communication (COM) port: it is used to connect communicating device like modem and mouse. This
transfers one bit data at a time. It needs a single wire to transmit 1 bit of
data. Hence it takes 8 times longer to transfer a byte. There are two types of
com ports, the 8-pin ports and 25-pins ports.
- Parallel
port: it is used to connect external input/output
devices like printers or scanners. Data transfer is usually one byte (8-bits)
at a time and it has 25 pins.
- IDE
(Integrated Digital Electronics) port: IDE
devices like CD-ROM drives or hard disk drives are connected to the mother
through the IDE port.
- USB
(Universal Serial Bus) port:
external peripheral devices such as printers, scanners, digital cameras, web
cameras, speakers etc. USB supports a data speed of 12 megabits per second,
supporting up to 127 devices.
20. What is
meant by shareware? Write its limitations.
Ans: software made available with the right to
redistribute copies, but it is stipulated that if one intends to use the
software, often after a certain period of time, then a license fee should be
paid.
Limitations of shareware:
- In shareware
the source code is not available.
- Modifications
to the software are not allowed.
21. Give the
memory representation for two dimensional array using Column Major Ordering.
Ans: In this method the elements are stored column wise, i.e. m elements of first column are stored in first m locations, m elements of second column are stored in next m locations and so on. E.g.
A 3 x 4 array will stored as below:
22. Give the
advantages of pointer.
Ans: - It is possible to write
efficient programs
-Memory
is utilized properly
-Dynamically
allocate and de-allocate memory
-Easy
to deal with hardware components
-Establishes
communication between program and data
23. Explain the
use of new and delete operators in pointers.
Ans: These operators allocate memory for objects
from a pool called the free store. The new operator calls the special function
operator new and the delete operator calls the special function operator delete
Example, to allocate memory
of type integer, int *iptr=new int;
To
allocate memory of type float, float *fptr=new float;
To allocate memory of type double, double *dptr=new
double;
Releasing dynamic memory
using delete as: delete iptr;
24. Explain the
advantages (features) of DBMS.
Ans: in the database approach, the
data is stored at a central location and is shared among multiple users. Thus,
the main advantage of DBMS is centralized data management. The advantages of
centralized database system are as follows:
-Controlled data redundancy: elimination of
duplication of data item in different files ensures consistency and saves the
storage space. The redundancy in the database cannot be eliminated completely
as there could be some performance and technical reasons for having some amount
of redundancy.
-Enforcing data integrity: data integrity
refers to the validity of data and it can be compromised in a number of ways.
-Data sharing: the data stored
in the database can be shared among multiple users or application programs. It
is possible to satisfy the data requirements of the new applications without
creating any additional data or with minimal modification.
-Ease of application development: the application
programmer needs to develop the application programs according to user’s needs.
The other issues like concurrent access, security, data integrity etc are
handled by the RDBMS itself.
-Data security: since the data
is stored centrally data security checks can be carried out whenever access is
attempted to sensitive data. To ensure security, a RDBMS provides security
tools such as used codes and passwords. Different checks can be established for
each type of access like addition, modification, deletion etc to each piece of
information in the database.
-Multiple user interfaces: For various
users having different technical knowledge DBMS provides different types of
interfaces such as query languages, application program interfaces, and
graphical user interfaces (GUI).
25. What is
e-commerce? Explain any two types.
Ans: e-commerce
is the trade of goods and services with the help of telecommunications and
computers.
- Business
to Business (B2B): Exchange of goods,
service and information between two business partners. Ex: Ebay.com
- Business
to Consumer: (B2C): Exchange of goods,
service and information from business to consumer. Ex: paytm.com
- Consumer
to Business: (C2B): Exchange of goods,
service and information from consumer to business. Ex: guru.com, freelancer.com
- Consumer
to Consumer: (C2C): Exchange of goods,
service and information between two consumers. Ex: olx.in
26. Expand UPS.
Explain the types of UPS.
Ans: electronic components of a computer system
require continuous supply of electric current for their operations to prevent
them from the failures, break down or shutdown.There are two types of power supply connected to a computer system; they are Switched Mode Power Supply (SMPS) and Uninterruptable Power Supply (UPS).
- SMPS: it converts AC power into DC power. It is a metal box in the rear of the system. It contains the power card plug and a fan for cooling, because it generates a lot of heat. SMPS with a power of 300 watts is needed. It converts 230 volts of AC to 5 to 12 DC volts and the wattage is around 180 to 300 watts, 450 watts and 500 watts.
- UPS: An UPS is a power supply that includes a battery to maintain power in the event of a power failure. An UPS keeps a computer running for several minutes to few hours after a power failure, enabling us to save data the is in RAM and then shut down the computer.
There are two types of UPS: Online UPS and standby UPS.
- Online UPS: it provides continuous power to the system from its own inverter when the power goes off. For a PC with color monitor 15”, requires an UPS of 500 VA and for a PC with color monitor 17”, requires an UPS of 600 VA.
- Standby UPS or Offline UPS: it monitors the power line and switches to battery power as soon as it detects a problem. The switch over to battery however, can require several milliseconds, during which time the computer is not receiving any power.
PART – D
IV. Answer any seven questions. Each question
carries 5 marks. (7
X 5 = 35)
27. Write an
algorithm to insert an element into a queue.
Ans: Step 1: if REAR=N then
PRINT
“overflow”
Exit
Step 2: if
FRONT=NULL then
FRONT=0
REAR=0
Else
REAR=REAR+1
Step
3: QUEUE[REAR]=ITEM
Step
4: return
28. Reduce
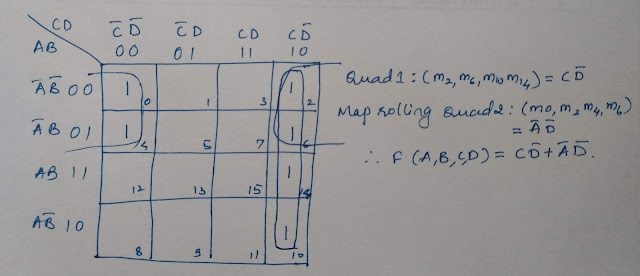
F(A,B,C,D)=∑(0,2,4,6,10,14) USING K-MAP.
Ans:
Ans: - stack is used to reverse a word.
- It is used in undo mechanism in text
editors.
- Conversion of decimal number into
binary.
- To solve tower of hanoi.
- Conversion of infix expression into
prefix and postfix.
- Quick sort.
- Run time memory management.
30. Write the
rules for to be followed in writing constructor function in C++.
Ans: - A constructor name is always same as
that of the class name
- There is no return type for the
constructors not even void
- A constructor should be declared in
public section
- A constructor is invoked automatically
when objects are created
- It is not possible to refer to the
address of constructors
- The constructors make implicit calls to
the operators new and delete when memory allocation is
required.
31. What is a
class? Write its declaration syntax and example.
Ans: a
class is a collection of object of similar type that share some common
properties among them.
Syntax of a class:
class class_name
{
private: data member;
function
member;
protected: data member;
function
member;
public: data member;
function member;
};
Example: class student
{
private: int rollno;
char
name[15];
float
percentage; public: void getdata();
void putdata();
};
32. What is a
friend function? Write the characteristics of a friend function.
Ans: friend function
is a non-member function that has full access right to private and protected
members of the class.
Characteristics of a friend function are
as follows:
- A
friend function has full access right to the private and protected members of
the class
- A
friend function cannot be called using the object of that class. It can be
invoked like any normal
function
- A
friend function can be declared anywhere in the class and it is not affected by
access specifiers
(private, protected and public)
- They
are normal external functions given special access privileges
- The
function is declared with keyword friend. But while defining friend function it
does not use
either friend or :: operator.
33. What is copy
constructor? Explain with syntax and programming example.
Ans: The
copy constructor is a
constructor which creates an object by initializing it with an object of the
same class.
The copy constructor is used to −
- Initialize one object from another of the same type.
- Copy an object to pass it as an argument to a function.
- Copy an object to return it from a function.
x a2=a1;
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class copy
{
int var;
public: copy(int temp)
{
var=temp;
}
int calculate()
{
int fact,i;
fact=1;
for(i=1;i<=var;i++)
fact=fact*i;
retrun fact;
}
}
int calculate()
{
int fact,i;
fact=1;
for(i=1;i<=var;i++)
fact=fact*i;
retrun fact;
}
};
void main()
{
int n;
cout<<”Enter the number: ”;
cin>>n;
copy obj(n);
copy cpy=obj;
cout<<”Before copying :
”<<n<<”!=”<<obj.calculate()<<endl;
cout<<”After copying :
”<<n<<”!=”<<cpy.calculate()<<endl;
}
34. Explain
network securities in detail.
Ans: Authorization: Authorization is the process of allowing an
authenticated users to access the resources by checking whether the user has
access rights to the system. Authorization helps you to control access rights
by granting or denying specific permissions to an authenticated user.- Authentication: Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user by obtaining some sort of credentials and using those credentials to verify the user's identity. If the credentials are valid, the authorization process starts. Authentication process always proceeds to Authorization process.
- Encrypted smart cards: Confidentiality is the use of encryption to protect information from unauthorized disclosure. Plain text is turned into cipher text via an algorithm, then decrypted back into plain text using the same method.
Cryptography is the method of converting data from a human readable form to a modified form,
and then back to its original readable form, to make unauthorized access difficult.
- Biometric systems: it involves unique aspects of a person’s body such as finger prints, retinal patterns, etc to establish his/her identity.
- Firewall: A firewall is a network security system designed to prevent unauthorized access to or from a private network. Firewalls can be implemented in both hardware and software, or a combination of both. Network firewalls are frequently used to prevent unauthorized internet users from accessing private networks connected to the Internet, especially intranets. All messages entering or leaving the intranet pass through the firewall, which examines each message and blocks those that do not meet the specified security criteria.
35. Explain the
differences between manual data processing and computerized (electronic) data
processing.
Ans:
Manual
data processing
|
Computerized
electronic data processing
|
The volume of data, which can be processed,
is limited.
|
The volume of data which can be processed
can be very large.
|
It requires large quantities of paper.
|
Reasonable, less amount of paper is used.
|
The speed and accuracy is limited.
|
The job executed is faster and accurate.
|
Labor cost is high.
|
Labor cost is economical.
|
Storage medium is paper.
|
Storage medium is secondary storage medium.
|
36. Explain any
five relational/comparison operators in SQL with suitable examples.
Ans: consider a=10 and b=20
Operator
|
Description
|
Example
|
=
|
Checks
if the values of two operands are equal or not, if yes then condition becomes
true.
|
(a=b)
is not true
|
!=
|
Checks
if the values of two operands are equal or not, if values are not equal then
condition becomes true.
|
(a!=b)
is true
|
>
|
Checks
if the value of left operand is greater than the value of right operand, if
yes then condition becomes true.
|
(a>b)
is not true
|
<
|
Checks
if the value of left operand is less than the value of right operand, if yes
then condition becomes true.
|
(a<b)
is true
|
>=
|
Checks
if the value of left operand is greater than or equal to the value of right
operand, if yes then condition becomes true.
|
(a>=b)
is not true
|
<=
|
Checks
if the value of left operand is less than or equal to the value of right
operand, if yes then condition becomes true.
|
(a<=b)
is true
|
37. Explain
briefly the types of inheritance.
Ans: - Single
inheritance: if a class is derived
from a single base class, it is called as single inheritance.- Multilevel inheritance: the classes can also be derived from the classes that are already derived. This type of inheritance is called multilevel inheritance.
- Multiple
inheritance: if a class is derived
from more than one base class, it is known as multiple inheritance.
- Hierarchical inheritance: if a number of classes are derived from a single
base class, it is called as hierarchical inheritance.
- Hybrid
inheritance: it is a combination of
Hierarchical and Multiple inheritance.
2nd puc computer science model 5 question papers and answers
 Reviewed by Vision Academy
on
January 18, 2020
Rating:
Reviewed by Vision Academy
on
January 18, 2020
Rating:
 Reviewed by Vision Academy
on
January 18, 2020
Rating:
Reviewed by Vision Academy
on
January 18, 2020
Rating:










No comments: