1st PUC COMPUTER SCIENCE LAB PROGRAMS PDF | class 11 computer science lab manual | 1st puc computer science programs
1st PUC COMPUTER SCIENCE LAB PROGRAMS PDF,1ST PUC COMPUTER SCIENCE LAB MANUAL,1ST PUC COMPUTER SCIENCE LAB MANUAL PDF, 1ST PUC COMPUTER SCIENCE LAB,1st puc computer science lab manual,1st puc computer science lab programs,1st puc computer science lab programs pdf,1st puc computer science lab manual pdf,1st puc computer lab manual pdf,1st puc lab manual computer science,1st puc lab manual computer science python,class 11 computer science lab manual pdf,class 11 computer science lab manual,class 11 computer science lab manual python,class 11 computer science practicals with solutions,class 11 computer science lab manual python free download,class 11 computer science lab manual python pdf download,class 11 computer science lab manual python pdf,class 11 computer science lab manual python pdf free download,1st puc computer science programs
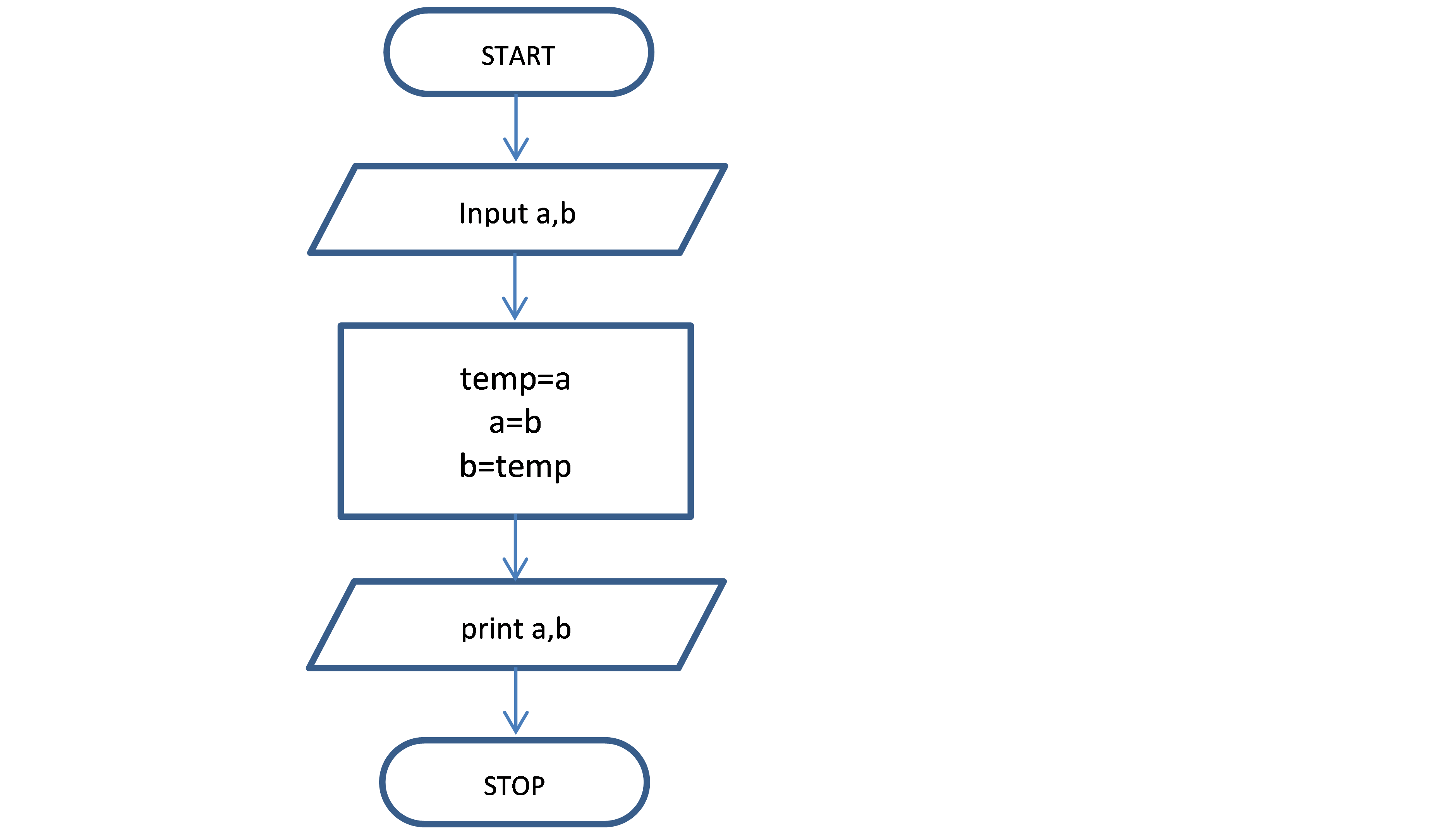
1. Write a program to swap two numbers
using a third variable.
Algorithm:
Step 1: START
Step 2: Input the first number → store it in a
Step 3: Input the second number → store it in b
Step 4: Display a and b before swapping
Step 5: Set temp = a
Step 6: Set a = b
Step 7: Set b = temp
Step 8: Display a and b after swapping
Step 9: STOP
Flowchart:
a=int(input("Enter the value of a:"))
b=int(input("Enter the value of b:"))
print("Before swapping a=",a," and b=",b)
temp=a
a=b
b=temp
print("After swapping a=",a," and b=",b)
1.
2. Write a program to enter two
integers and perform all arithmetic operations on them.
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Input the first number and store it in variable a
Step 3: Input the second number and store it in variable b
Step 4: Compute sum = a + b
Step 5: Compute diff = a - b
Step 6: Compute prod = a * b
Step 7: Compute divi = a // b
Step 8: Compute modulus = a % b
Step 9: Print "Addition =", sum
Step 10: Print "Subtraction =", diff
Step 11: Print "Multiplication =", prod
Step 12: Print "Division =", divi
Step 13: Print "Modulus =", modulus
Step 14: Stop
Flowchart:
a=int(input("Enter the value of a:"))
b=int(input("Enter the value of b:"))
sum=a+b
diff=a-b
prod=a*b
divi=int(a/b)
modulus=a%b
print("Addition=", sum)
print("Subtraction=",diff)
print("Multiplication=",prod)
print("Division=",divi)
print("Modulus=",modulus)
1.
3. Write a Python program to accept
length and width of a rectangle and compute its perimeter and area.
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Input the length of the rectangle and store it in l
Step 3: Input the width of the rectangle and store it in w
Step 4: Calculate the area using formula area = l * w
Step 5: Calculate the perimeter using formula perimeter = 2 * (l + w)
Step 6: Display the value of area
Step 7: Display the value of perimeter
Step 8: Stop
Flowchart:
l=float(input("Enter the length of the rectangle:"))
w=float(input("Enter the width of the rectangle:"))
area=l*w
perimeter=2*(l+w)
print("Area of rectangle=",area)
print("Perimeter of rectangle=",perimeter)
4. Write a python program to calculate
the amount payable if money has been lent on simple interest. Principal or
money lent=P, Rate of interest =R% per annum and Time =T years. Then simple
interest (SI) =PxTxR/100. Amount payable=Principal+SI. P,R and T are given as
input to the program.
Algorithm:
Step 1: START
Step 2: INPUT principal amount and store it in variable P
Step 3: INPUT time and store it in variable T
Step 4: INPUT rate of interest and store it in variable R
Step 5: COMPUTE Simple Interest using the formula:
SI = (P × T × R) / 100
Step 6: PRINT Simple Interest (SI)
Step 7: STOP
Flowchart:
p=float(input("Enter the principal amount:"))
t=float(input("Enter the time:"))
r=float(input("Enter the rate of interest:"))
si=p*t*r/100
print("Simple Interest=",si)
1.
5. Write a program to find the largest
among three numbers.
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Input the first number and store it in variable a
Step 3: Input the second number and store it in variable b
Step 4: Input the third number and store it in variable c
Step 5: If a is greater than or equal to both b and c, then
Set large = a
Step 6: Else if b is greater than or equal to both a and c, then
Set large = b
Step 7: Else
Set large = c
Step 8: Print the value of large
Step 9: Stop
Flowchart:
a=float(input("Enter the value of a:"))
b=float(input("Enter the value of b:"))
c=float(input("Enter the value of c:"))
if(a>=b)and(a>=c):
large=a
elif(b>=a)and(b>=c):
large=b
else:
large=c
print("The largest number=",large)
6. Write a program that takes the name
and age of the user as input and displays a message whether the user is
eligible to apply for a driving license or not. (The eligible age is 18 years).
Algorithm:
Step 1: START
Step 2: INPUT name
Step 3: INPUT age
Step 4: IF age >= 18 THEN
PRINT "Hello, <name>! You are eligible."
ELSE
PRINT "Sorry, <name>. You are not eligible yet."
Step 5: STOP
Flowchart:
name=input("Enter your name: ")
age=int(input("Enter your age: "))
if age>=18:
print("Hello,
",name," ! You are eligible.")
else:
print("Sorry,
",name,". You are not eligible yet.")
7. Write a program that prints minimum and maximum of five numbers entered by the user.
Algorithm:
Step 1: START
Step 2: SET small = 0, large = 0
Step 3: REPEAT steps 4 to 7 for i = 1 to 5
Step 4: INPUT a number and store it in 'a'
Step 5: IF i = 1 THEN
SET small = a
SET large = a
Step 6: IF a < small THEN
SET small = a
Step 7: IF a > large THEN
SET large = a
Step 8: PRINT "Smallest number = ", small
Step 9: PRINT "Largest number = ", large
Step 10: STOP
Flowchart:
small=0
large=0
for i in range(0,5):
a=int(input("Enter the
number "+str(i+1)+":"))
if i==0:
small=large=a
if(a<small):
small=a
if(a>large):
large=a
print("Smallest number=",small)
print("Largest number=",large)
Watch Explainer Video Here
8. Write a python program to find the
grade of a student when grades are allocated as given in the table below.
Above 90% A
80% to 90% B
70% to 80% C
60% to 70% D
Below 60% E
Percentage of the marks obtained by the student is input to the program.
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Input the percentage and store it in variable p
Step 3: If p > 90, then
Print "Grade A"
Step 4: Else if p > 80, then
Print "Grade B"
Step 5: Else if p > 70, then
Print "Grade C"
Step 6: Else if p > 60, then
Print "Grade D"
Step 7: Else
Print "Grade E"
Step 8: Stop
Flowchart:
p=float(input("Enter the percentage: "))
if(p>90):
print("Grade A")
elif(p>80):
print("Grade
B")
elif(p>70):
print("Grade
C")
elif(p>60):
print("Grade
D")
else:
print("Grade
E")
1.
9. Write a function to print the table
of a given number. The number has to be entered by the user.
Algorithm:
Start
Step 1: Input a number and store it in variable a
Step 2: Set i = 1
Step 3: Repeat steps 4 to 6 while i <= 10
Step 4: Compute b = a * i
Step 5: Display the result in the format a x i = b
Step 6: Increment the value of i by 1
Stop
Flowchart:
a=int(input("Enter the number: "))
i=1
while i<=10:
b=a*i
print(a,'x',i,'=',b)
i=i+1
1.
10. Write a program to find the sum of
digits of an integer number, input by the user.
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: INPUT the number and store in variable n
Step 3: SET sum = 0
Step 4: WHILE n > 0, repeat Steps 5 to 7
Step 5: rem = n % 10 ← (Get the last digit)
Step 6: sum = sum + rem ← (Add the digit to sum)
Step 7: n = n // 10 ← (Remove the last digit)
Step 8: PRINT "The sum of digits =", sum
Step 9: Stop
Flowchart:
n=int(input("Enter the number: "))
sum=0
while n>0:
rem=n%10
sum=sum+rem
n=n//10
print("The sum of digits=",sum)
1.
11. Write a program to check whether an
input number is a palindrome or not.
Algorithm:
Step 1: START
Step 2: Input a number and store it in variable n
Step 3: Store the value of n in another variable temp (for comparison later)
Step 4: Set rev = 0 to store the reversed number
Step 5: Repeat the following steps while n > 0:
a) Find the last digit using digit = n % 10
b) Add this digit to rev by shifting existing digits: rev = rev * 10 + digit
c) Remove the last digit from n using n = n // 10
Step 6: After the loop ends, compare temp and rev:
If temp == rev then
PRINT "It is a palindrome"
Else
PRINT "It is not a palindrome"
Step 7: STOP
Flowchart:
n=int(input("Enter a number: "))
temp=n
rev=0
while(n>0):
digit=n%10
rev=rev*10+digit
n=n//10
if(temp==rev):
print("It is a
palindrome")
else:
print("It is not
a palindrome")
1.
12. Write a program to print the
following patterns:
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4
1 2 3
1 2
1
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Input the number of rows (n)
Step 3: Repeat steps 4 to 6 while i goes from n to 1
Step 4: Set j = 1
Step 5: Repeat step 6 while j <= i
Step 6: Print j and increment j by 1
Step 7: Move to the next line
Step 8: Decrease i by 1 and repeat
Step 9: Stop
Flowchart:
n=int(input("Enter the number of rows: "))
for i in range(n,0,-1):
for j in range(1,i+1):
print(j,end=' ')
print()
1.
13. Write a program that uses a user
defined function that accepts name and gender (as M for male, F for Female) and
prefixes Mr./Ms. Based on the gender.
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Input name of the student
Step 3: Input gender of the student
Step 4: Check if gender is 'M' or 'm'
→ If yes, then display "Mr." followed by name
Step 5: Otherwise, check if gender is 'F' or 'f'
→ If yes, then display "Ms." followed by name
Step 6: Otherwise, display "Please enter only M or F in gender"
Step 7: Stop
Flowchart:
def student(name,gender):
if(gender=='M' or
gender=='m'):
print('Mr.',name)
elif(gender=='F' or
gender=='f'):
print('Ms.',name)
else:
print("Please
enter only M or F in gender")
name=input("Enter the name: ")
gender=input("Enter the gender M for Male and F for Female: ")
student(name,gender)
1.
14. Write a program that has a user
defined function in accept the coefficients of a quadratic equation in
variables and calculates its determinant. For example : if the coefficients are
stored in the variables a,b,c then calculate determinant as b2 –
4ac. Write the appropriate condition to check determinants on positive, zero
and negative and output appropriate result.
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Input the value of a
Step 3: Input the value of b
Step 4: Input the value of c
Step 5: Compute d = b² - 4 × a × c
Step 6: If d > 0, then
Print “The roots are real and different”
Step 7: Else if d == 0, then
Print “The roots are real and equal”
Step 8: Else
Print “The roots are imaginary”
Step 9: Stop
a=int(input("Enter the value of a: "))
b=int(input("Enter the value of b: "))
c=int(input("Enter the value of c: "))
def disc(a,b,c):
d=b**2-4*a*c
return d
det=disc(a,b,c)
if(det>0):
print("The roots
are real and different")
elif(det==0):
print("The roots
are real and equal")
else:
print("The roots
are imaginary")
1.
15. Write a program that has a user
defined function to accept 2 numbers as parameters, if number is less than number 2 then numbers are
swapped and returned, i.e., number 2 is returned in place of number 1 and
number 1 is reformed in place of number 2, otherwise the same order is returned.
Algorithm:
Step 1: START
Step 2: Input the first number and store it in variable a
Step 3: Input the second number and store it in variable b
Step 4: Display the values of a and b before swapping
Step 5: Check if a is less than b
If YES, then set a = b and b = a
If NO, keep a and b as it is
Step 6: Display the values of a and b after swapping
Step 7: STOP
def swap(a,b):
if(a<b):
return
b,a
else:
return
a,b
a=int(input("Enter the value of a: "))
b=int(input("Enter the value of b: "))
print("Before swapping a=",a," and b=",b)
a,b=swap(a,b)
print("After swapping a=",a," and b=",b)
Watch Explainer Video Here
s1=s.title()
print("The input string
in title case is:",s1)
name=input("Enter the string:")
space=0
for b in name:
if b.isspace():
space+=1
if name.istitle():
print("The string is
already in title case")
elif space>0:
student(name)
else:
print("The string is in
one word")
18. Write a function that takes a sentence as an input parameter where each word in the sentence is separated by a space. The function should replace each blank with a hyphen and then return the modified sentence.
return s.replace(' ','-')
s1=input("Enter the sentence:")
s2=replace1(s1)
print("The modified sentence=",s2)
19. Write a program to fund the number of times an element occurs in the list.
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Store the numbers [10, 20, 10, 40, 50, 30, 10, 10, 50] in a list
Step 3: Display all the elements of the list
Step 4: Ask the user to enter a number (this is the number we want to count)
Step 5: Count how many times the entered number appears in the list
Step 6: Display the result showing how many times the number appears
Step 7: Stop
Flowchart:
list=[10,20,10,40,50,30,10,10,50]
print("Elements in the list are:",list)
a=int(input("Enter the number to check how many times the element
occurs in the list:"))
b=list.count(a)
print("An element ",a," is present ",b,"
times")
20. Write a function that returns the largest element of the list passed as parameter.
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Create a list of numbers
Step 3: Set a variable n = 0 to store the largest number temporarily
Step 4: Repeat the following steps for each element in the list:
a) Check if it's the first element or the current element is greater than n
b) If yes, update the value of n with the current element
Step 5: After the loop ends, n will hold the largest number
Step 6: Display the list
Step 7: Display the largest number
Step 8: Stop
Flowchart:
n=0
for i in range(len(list)):
if(i==0 or list[i]>n):
n=list[i]
return n
list=[10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100]
max=large(list)
print("The elemtns of the list are:",list)
21. Write a program to read a list of elements. Modify this list so that it does not contain any duplicate elements, i.e. all elements occurring multiple times in the list should appear only once.
newlist=[]
for a in range(len(list)):
if list[a] not in newlist:
newlist.append(list[a])
return newlist
list=[]
n=int(input("How many elements?"))
print("Enter the elements:")
for i in range(n):
a=int(input())
list.append(a)
print("The numbers in list:",list)
print("List without duplicate elements is:",dup(list))
22. Write a program to read email IDs of n number of students and store them in a tuple. Create two new tuples, one to store only the usernames from the email IDs and second to store domain names from the email IDs. Print all three tuples at the end of the program. [Hint: You may use the function split()]
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Create an empty tuple named email
Step 3: Create an empty tuple named username
Step 4: Create an empty tuple named domainname
Step 5: Ask the user how many email IDs they want to enter
Step 6: Store the input number in variable n
Step 7: Repeat the following steps from i = 1 to n:
Step 7.1: Ask the user to input the i-th email ID and store it in variable eid
Step 7.2: Add eid to the email tuple
Step 7.3: Split eid at the “@” symbol
Step 7.4: Take the first part (before @) and add it to the username tuple
Step 7.5: Take the second part (after @) and add it to the domainname tuple
Step 8: Print the tuple email
Step 9: Print the tuple username
Step 10: Print the tuple domainname
Step 11: Stop
Flowchart:
email=tuple()
username=tuple()
domainname=tuple()
n=int(input("How
many valid email IDs you want to enter? "))
for i in
range(n):
eid=input("Please enter email id"+str(i+1)+": ")
email+=(eid,)
e=eid.split("@")
username=username+(e[0],)
domainname=domainname+(e[1],)
print("The
IDs in the tuple:",email)
print("The
username of email ids are: ",username)
print("The domain
name of email ids are: ",domainname)
23. Write a program to input names of n students and store them in a tuple. Also, input a name from the user and find if this student is present in the tuple or not.
Algorithm:
Step 1: START
Step 2: Create an empty tuple called name
Step 3: INPUT total number of names as n
Step 4: Repeat Steps 5 to 6 n times
Step 5: INPUT a name and store it in variable num
Step 6: Add num to the tuple name
Step 7: PRINT all names entered
Step 8: INPUT the name to be searched and store it in search
Step 9: IF search is in name THEN
PRINT "Name is present"
Step 10: ELSE
PRINT "Name is not present"
Step 11: STOP
Flowchart:
name=tuple()
n=int(input("How many names do you want to
enter?"))
for i in range(n):
num=input("Enter the name"+str(i+1)+": ")
name=name+(num,)
print("Names entered are:",name)
search=input("Enter the name to be searched:
")
if search in name:
print("Name",search,"is present")
else:
print("Name",search,"is not present")
24. Write a program to create a dictionary from a string. Note: Track the count of the letters from the string. Sample string : ‘2nd pu course’. Expected output : {‘ ‘:2,’2’:1,’n’:1,’d’:1,’o’:1,’p’:1.’u’:2,’c’:1,’s’:1,’r’:1.’e’:1}
Step 2: Store the string "2nd pu course" in variable s
Step 3: Create an empty dictionary called s1
Step 4: Repeat steps 5–7 for each character in the string s:
Step 5: If the character is already in the dictionary s1, then
INCREMENT the count of that character by 1
Step 6: Otherwise
ADD the character to dictionary s1 with value 1
Step 7: End of loop
Step 8: Display the dictionary s1
s="2nd pu course"
print("The input string is:",s)
s1=dict()
for character in s:
if
character in s1:
s1[character]+=1
else:
s1[character]=1
print("The dictionary created from characters of the
string is:",s1)
 Reviewed by Vision Academy
on
October 21, 2022
Rating:
Reviewed by Vision Academy
on
October 21, 2022
Rating:



























%20of%20text%20from%20the%20user%20until%20enter%20is%20pressed.png)


















No comments: